Transcranial Doppler and Patent Foramen Ovale(PFO)
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a hole between the left and right atria (upper chambers) of the heart. This hole exists in everyone before birth, but most often closes shortly after being born. PFO is what the hole is called when it fails to close naturally after a baby is born. Nearly 1 in 4 has PFO, but many do not know they have the condition.
Most patients with a PFO do not have any symptoms. However, the condition may play a role in migraine headaches and it increases the risk of stroke, transient ischemic attack and heart attack.
TCD has been proven to be a good screening tool for evaluating PFO. It is not invasive, fast, does not require patient sedation and provides reproducible results that are easy to interpret. TCD uses power M-mode Doppler insonation of the basal cerebral arteries to detect micro-bubbles (MBs) that have crossed right-to-left into the systemic circulation. The usual technique is an insonation of middle cerebral artery (MCA), once it represents the main thromboembolic site. The direct involvement of the neurologist in performing this test represents an advantage of TCD over TEE and TTE, in addition to increased patient comfort (compared with TEE), semi quantitative assessment of shunt size, and, possibly, suggests an extracardiac or intracardiac shunting. Moreover, c-TCD enables improved quantification of micro-embolic signals, by using provocative maneuvers, as the patient is more comfortable and therefore more amenable to undergo an adequate Valsalva maneuver. Another advantage is the fact that TCD can monitor in real time the spontaneous passage of microemboli during prolonged monitorization without a provocative test, which can detect the embolic phenomenon as it takes place.

Delica TCD for the PFO (bubble test)
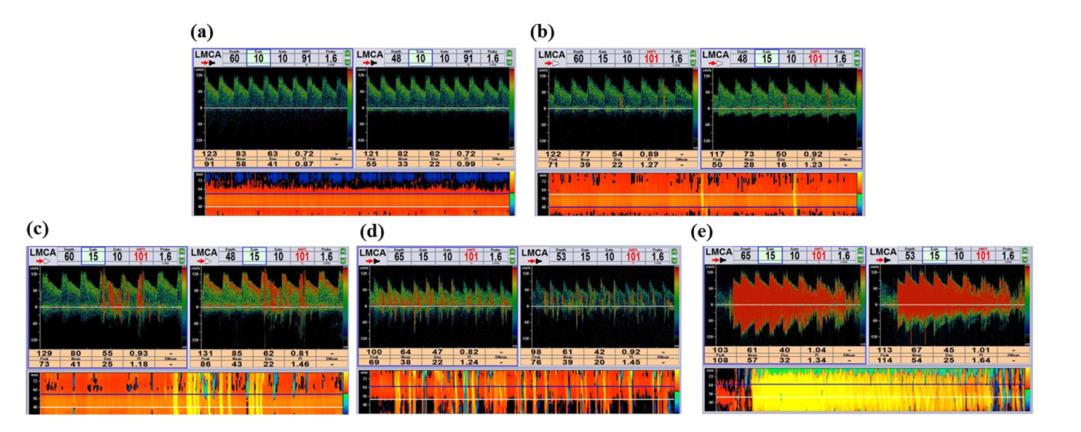
The five-level right-to-left shunt categorization according to microbubble (MB) count in the contrast-enhanced transcranial Doppler spectrum using unilateral middle cerebral artery monitoring.
Grade 0 = negative (a); Grade I = 1 < MBs <10 (b); Grade II = 10 < MBs < 25 (c); Grade III = >25 MBs and no curtain (d); Grade IV = curtain (where a single bubble cannot be identified) (e)
-Unique Robotic monitoring probe for bilateral monitoring (comfortable)
-Power Dynamic M mode display, high resolution (128depth combined into 8000 gates) to detect micro-bubbles (MBs) that have crossed right-to-left into the systemic circulation.
-Intelligent classification for the PFO results according to the MES count.
Reference:
1.Right-to-left shunt detected by TCD and a comparison of provocation maneuvers.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175049 April 6, 2017
2.Latin American Consensus Statement for the Use of Contrast-Enhanced Transcranial Ultrasound as a Diagnostic Test for Detection of Right-to-Left Shunt Cerebrovasc Dis 2019;48:99–108
3.© 2010 Intermountain Healthcare
Publication:
Prevalence and extent of right-to-left shunt in migraine: a survey of 217 Chinese patients